Inroduction For Web Design
Web design is a multidisciplinary field that involves the creation and maintenance of websites. It encompasses a wide range of skills, techniques, and tools to produce visually appealing and functional websites. In this article, we will delve into the details of web design, covering various aspects from its importance to the key principles and technologies involved.
1. Importance of Web Design:
Web design is crucial for several reasons:
Aesthetic Appeal: The visual design of a website plays a significant role in attracting and retaining visitors. A well-designed website with an appealing layout, color scheme, and typography can leave a positive impression on users.
User Experience (UX): Web design directly impacts the user experience. A well-designed website is easy to navigate, user-friendly, and provides a seamless experience for visitors. It enhances usability and encourages visitors to stay longer and explore more.
Branding: Your website is often the first point of contact with potential customers or clients. Consistent branding, including logos, color schemes, and typography, helps reinforce your brand identity and recognition.
Functionality: Effective web design ensures that a website functions smoothly, with all its features and functionalities working as intended. This includes responsive design for mobile users and accessibility for people with disabilities.
Conversion: Web design can influence conversion rates, whether it's getting users to make a purchase, sign up for a newsletter, or contact your business. A well-designed website can optimize these conversion paths.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization): The structure and layout of a website impact its search engine rankings. Proper web design practices, such as optimizing page load times and using SEO-friendly coding techniques, can improve a site's visibility in search engine results.
2. Key Principles of Web Design:
Successful web design is guided by several fundamental principles:
Visual Hierarchy: Designers use visual hierarchy to prioritize and organize content. This involves arranging elements like headings, images, and buttons in a way that guides users' attention and makes it clear what's most important.
Balance: Achieving visual balance ensures that the elements on a page are harmonious and don't overwhelm the user. Balance can be achieved through the distribution of elements, including text, images, and white space.
Typography: Selecting the right fonts and typography is essential for readability and conveying the website's tone. Designers choose fonts that match the brand's personality and ensure that text is legible on various devices.
Color Theory: Colors evoke emotions and play a vital role in web design. Designers carefully select color palettes that resonate with the brand and create a pleasing visual experience. Colors also help with branding and navigation cues.
Consistency: Consistency in design elements, such as headers, navigation menus, and buttons, enhances user understanding and familiarity with the site. It also reinforces the brand's identity.
Whitespace: Whitespace, or negative space, is the empty area around elements on a page. It's crucial for readability and preventing visual clutter. Adequate whitespace makes content easier to digest.
Responsive Design: With the increasing use of mobile devices, responsive web design is essential. It ensures that a website looks and functions well on a variety of screen sizes and devices.
Accessibility: Web design should be inclusive and accessible to people with disabilities. This includes providing alternative text for images, keyboard navigation, and clear, understandable content.
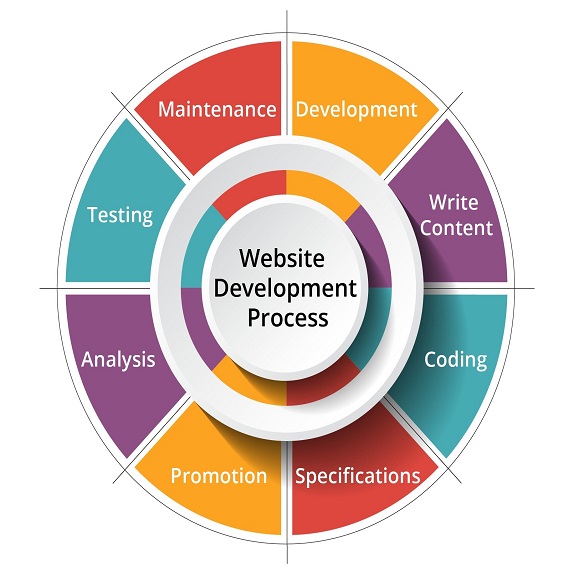
3. Web Design Process:
The web design process typically involves several stages:
1. Planning: In this phase, designers and stakeholders define the website's goals, target audience, and overall structure. They create a sitemap and plan the content and features.
2. Wireframing: Wireframes are simple, low-fidelity sketches that outline the layout and structure of each page. They help visualize the placement of elements and content.
3. Design: This phase involves creating high-fidelity mockups or prototypes of the website. Designers focus on visual aesthetics, typography, color schemes, and imagery. Tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, or Figma are often used in this stage.
4. Development: Developers use coding languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to bring the design to life. They make sure the website is responsive, loads quickly, and functions correctly.
5. Testing: Extensive testing is crucial to ensure the website works across different browsers and devices. It also involves checking for functionality issues and identifying and fixing any bugs.
6. Launch: Once the website passes testing and quality assurance, it's ready for launch. This involves setting up hosting, domain registration, and making the site accessible to the public.
7. Maintenance: Web design is an ongoing process. After launch, regular maintenance is necessary to update content, fix issues, and adapt to changing technology and user needs.
4. Web Design Technologies:
Several technologies are fundamental to web design:
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): HTML is the markup language used to structure the content of web pages. It defines the elements and their layout on a page.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS is used to control the visual presentation of web pages. It allows designers to apply styles, such as colors, fonts, and layout, to HTML elements.
JavaScript: JavaScript is a scripting language that enables interactive and dynamic features on websites. It's used for things like form validation, animations, and interactivity.
Responsive Frameworks: Frameworks like Bootstrap and Foundation provide pre-designed and customizable templates and components, making it easier to create responsive websites.
Content Management Systems (CMS): CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal simplify website creation and management by providing tools for content editing and organization.
Graphic Design Software: Tools like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and Sketch are essential for creating graphics and images used in web design.
Version Control: Version control systems like Git help teams collaborate on web design projects by tracking changes, enabling version control, and facilitating collaboration.
Web Hosting: A web hosting service is required to store and serve the website files to users on the internet.
5. Trends in Web Design:
Web design is a dynamic field, and it evolves over time. Some recent trends include:
Mobile-First Design: Given the prevalence of mobile devices, designers prioritize mobile-friendly layouts and responsive design.
Minimalism: Minimalist design emphasizes simplicity and clean layouts, focusing on essential elements and reducing visual clutter.
Dark Mode: Dark mode or dark-themed designs are gaining popularity for their aesthetic appeal and potential energy-saving benefits on OLED screens.
Microinteractions: These subtle animations and interactions enhance user engagement and provide feedback in real-time.
Illustrations and Custom Graphics: Custom illustrations and graphics are used to create unique and memorable visual experiences.
AI and Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants improve user interactions and provide customer support.
6. Conclusion:
Web design is a dynamic and essential field that combines creativity, technology, and user experience to create effective websites. Understanding the principles of web design, utilizing the right technologies, and staying current with design trends are key to producing visually appealing, functional, and user-friendly websites. As the internet continues to evolve, web design will play a critical role in shaping online experiences and promoting businesses and organizations worldwide.